Com o Tmux é possível executar múltiplas sessões do terminal em uma única janela. Isso é muito útil quando se trabalha com apenas 1 monitor ou precisa alterar entre as sessões rapidamente. Abaixo vou detalhar a instalação e principais comandos.
Instalação
Para distros baseadas em Debian, como o Ubuntu, abra o terminal e execute:
sudo apt-get install tmux
/***/
Executando o Tmux
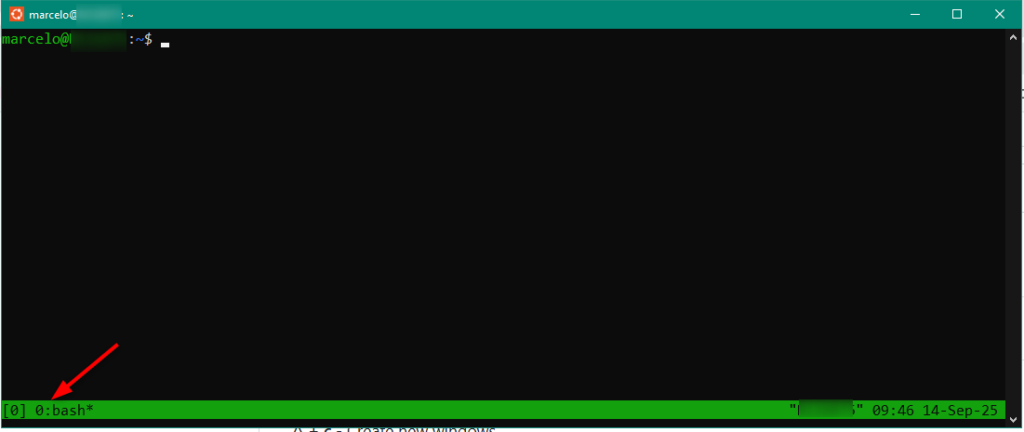
Após instalação, digite “tmux” no terminal para executá-lo:

Será exibida uma barra, na parte inferior da tela, exibindo o número da sessão e o comando em execução. Neste caso ‘0:bash‘:
- Número sessão: 0
- Comando: bash
/***/
Criando sessão
Pressione ‘Ctrl + B‘ e sequência digite ‘c‘. Na barra inferior será exibindo o número atribuído para ela, no caso ‘1:bash‘:

Repare que o sinal ‘*‘ saiu da janela ‘0:bash‘ para ‘1:bash‘. Este sinal indica a sessão ativa que executará os comandos.
/***/
Alternando entre as sessões
Para alternar utilize os comandos:
- ‘Ctrl + B‘ e sequência digite ‘n‘: Alterna para a próxima sessão;
- ‘Ctrl + B‘ e sequência digite ‘p‘: Alterna para a sessão anterior.
No exemplo abaixo a sessão ‘0:bash‘ exibe as informações da release e na ‘1:bash‘ é executado o comando htop. As sessões são alternadas e seus estados são mantidos:
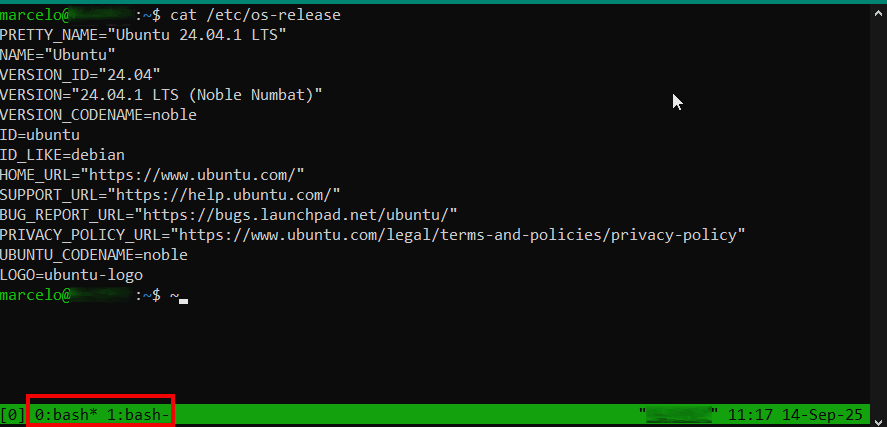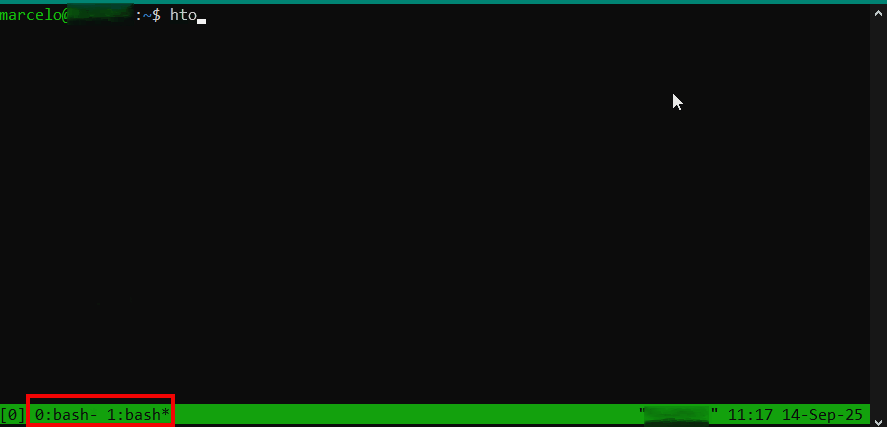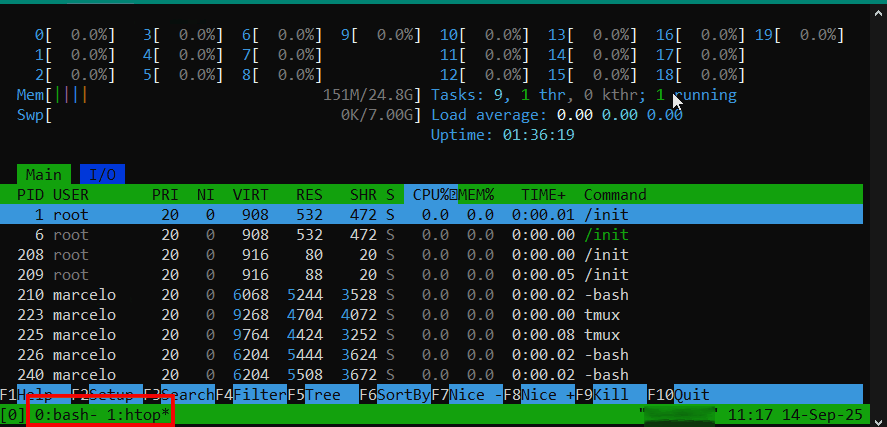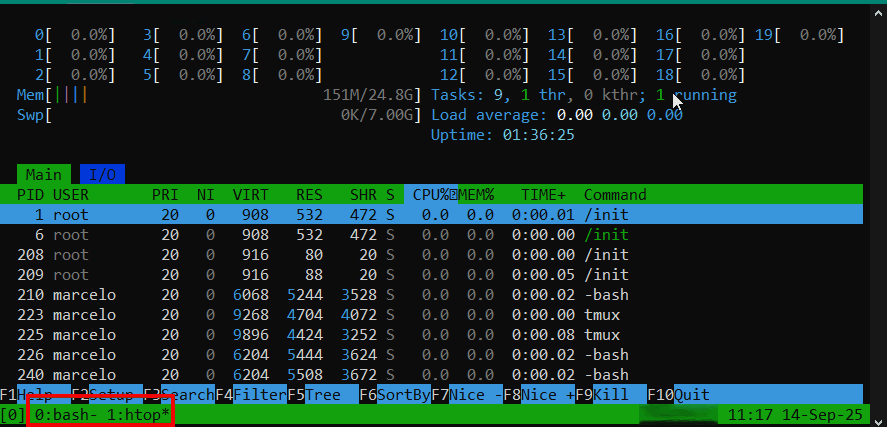
Para encerrar a sessão, basta acessá-la e executar o comando ‘exit‘.

Também é possível executar um ‘detached‘ para sair das sessões, mas mantê-las em execução. Desta forma será possível acessá-las novamente.
/***/
Detached da sessão
Execute o comando ‘Ctrl + B‘ e sequência digite ‘d‘. A barra inferior do Tmux será fechada e a sessão continuará em execução no backgound:

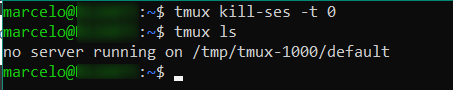
Para listar a sessões ativas em background, execute:
tmux ls
Cada sessão possui um número. Para voltar para a sessão, execute:
tmux a -t [número da sessão]
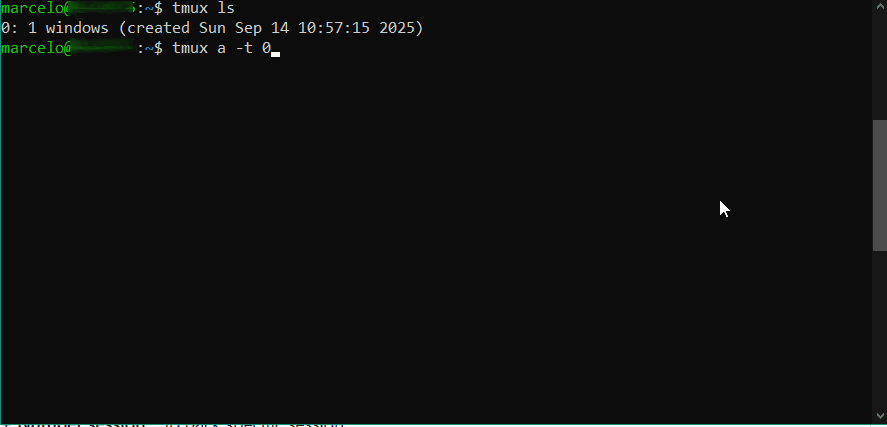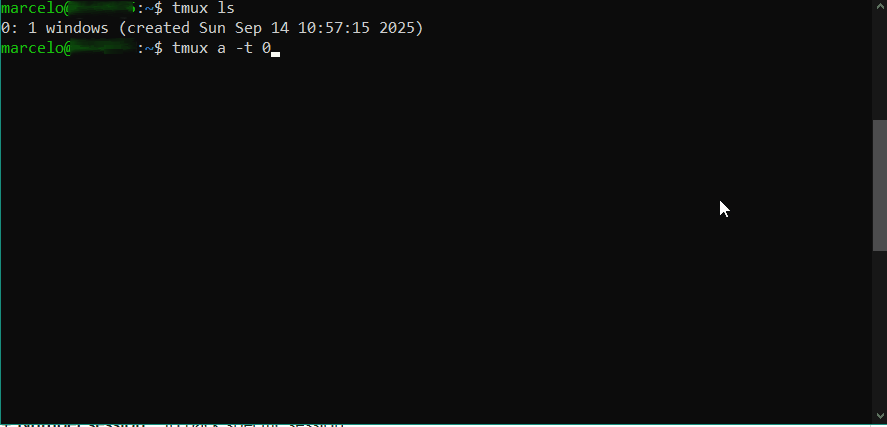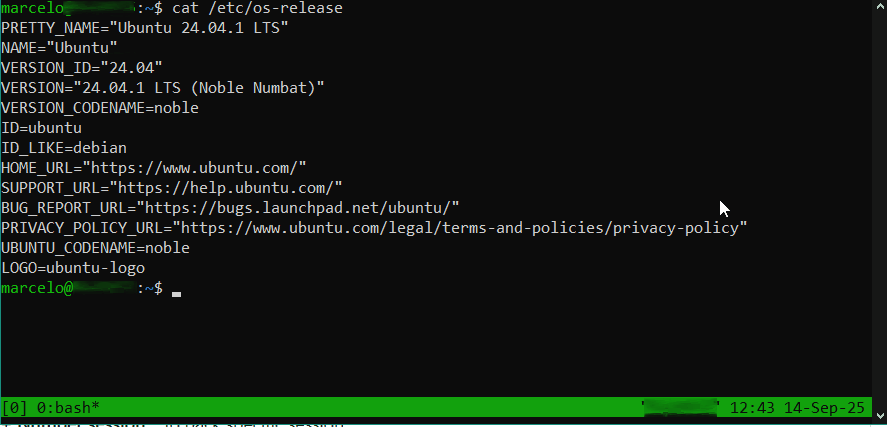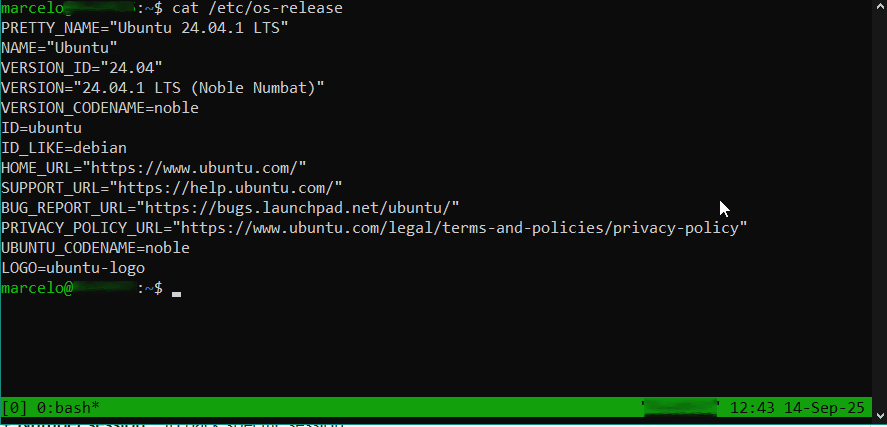
Para encerrar a sessão, execute:
tmux kill-ses -t [número da sessão]
/***/
Em breve irei publicar a parte 2 sobre segmentação da janela de forma horizontal e vertical.

Materiais de referência:
English version
With Tmux, it is possible to run multiple terminal sessions in a sigles window. This is useful when working on one screen or when you need to switch between sessions quickly. Below, I will explain how to install it and the mais commands.
Install
On linux distributions based on Debian, such as Ubuntu, open the terminal and run:
sudo apt-get install tmux
/***/
Execute Tmux
Before installing, type “tmux” in the terminal:

It will show a bar at the bottom of the screen with the session number and the running command. In this case ‘0:bash‘:
- Number session: 0
- Command: bash

/***/
Create session
Press ‘Ctrl + B‘, then type ‘c‘. At the bottom bar, you will see a new session number. In this case ‘1:bash‘:

Notice that the ‘*‘ symbol moved from ‘0:bash‘ to ‘1:bash‘. This symbol shows active session.
/***/
Switch between sessions
To switch, use the following commands:
- ‘Ctrl + B‘, then type ‘n‘: Switch to the next session;
- ‘Ctrl + B‘, then type ‘p‘: Switch to the previous session.
In the example below, session ‘0:bash‘ shows release information, and session ‘1:bash‘ is running htop. The sessions are switched, but their states are preserved.

To kill a session, open the session and type ‘exit‘.
It is also possible to ‘detached‘ from a session to exit it while keeping it running. This way, you can go back to it later.
/***/
Detached session
Type ‘Ctrl + B‘, then type ‘d‘. The bottom bar will disappear, and the session will continue running in the background.

To list the sessions running in the background, type:
tmux ls
Each session has a number. To go back to a session, type:
tmux a -t [number session]

To kill a session type:
tmux kill-ses -t [number session]

/***/
Soon I will create part two of this post about splitting the window horizontally and vertically.

Reference:
